-
€


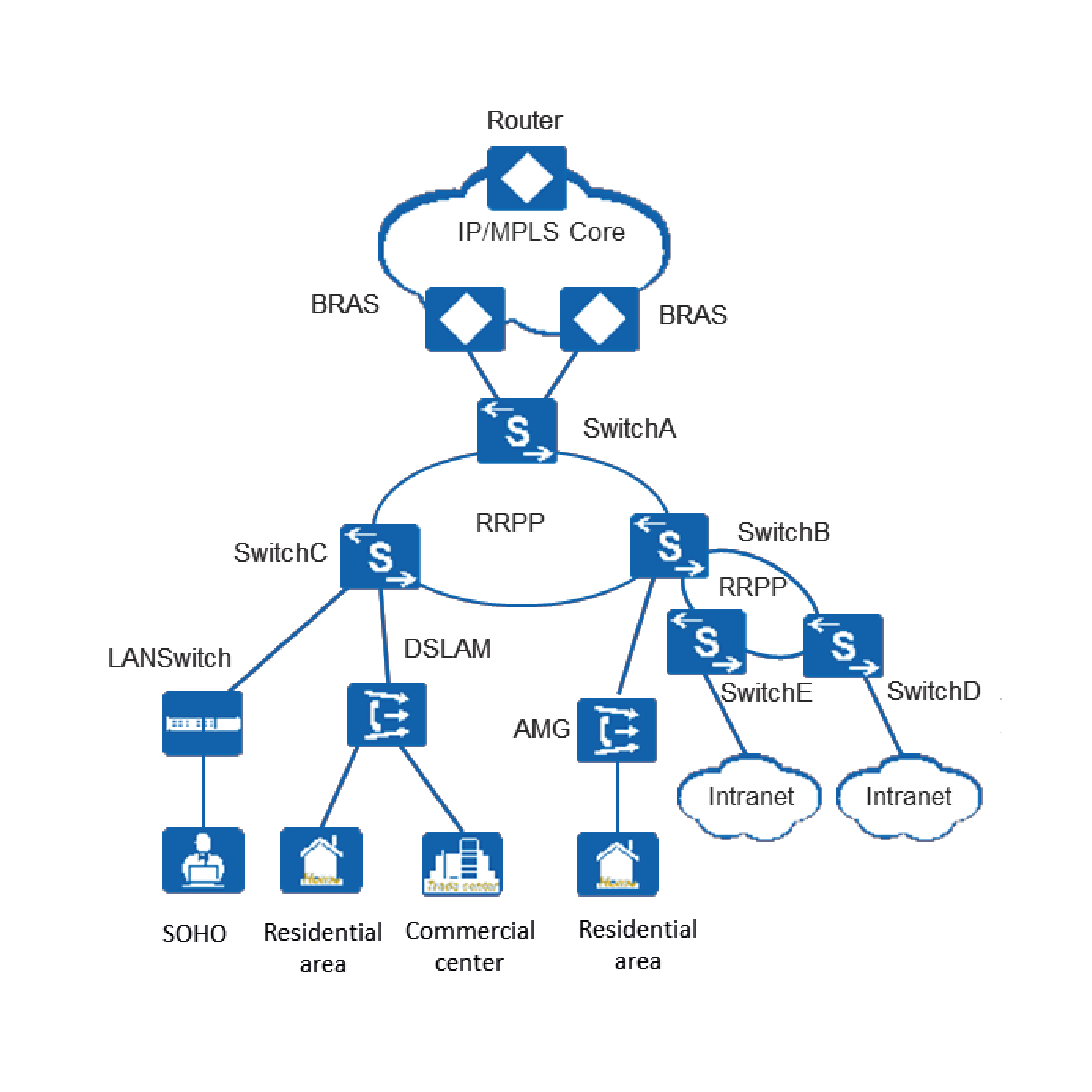
The Huawei S6730-H24X6C is an enterprise-class switch from the CloudEngine family. It features 24 SFP+ slots (10 Gbps) and 6 QSFP28 slots (100 Gbps), and stands out with its advanced management capabilities. It provides full routing support, including BGP and BGP4+, MPLS support, SVF, and advanced security features. It can function as a WAC – Wireless Access Controller – and operate as a controller for access points, helping to reduce the number of devices used in the network. The device is designed for ISP applications, as an aggregation switch in large campus networks, or as an access switch in a data center. Due to its extensive management capabilities and high throughput, the S6730-H24X6C can be used as a core switch in most smaller networks.
The device features a chassis suitable for mounting in a 19" rack, with necessary mounting accessories included. Active cooling is implemented using 4 fan modules with front-to-back airflow – air is drawn in from the port side and expelled at the rear. The package includes two PDC1000S12 power supply modules, which can operate redundantly; if one fails, the other takes over. The input voltage range is 100 – 240 V, the maximum power consumption of the switch is 254 W, and the typical power consumption at 30% load is 149 W.

CloudEngine S6730-H Series
The offered product is a switch from the CloudEngine family, specifically the S6730-H series. It provides advanced Layer 3 management features and supports routing, including BGP and BGP4+. It enables real-time monitoring of packet loss and network performance using iPCA technology and the TWAMP protocol. The device supports VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol), allowing the implementation of a backup uplink connection. The S6730-H can be connected to multiple other switches using multiple links.
The device supports iStack – intelligent stacking, which allows multiple switches to be combined into a single unit (from a management perspective). Management panel access is available via the cloud or through several other methods (a full list is provided in the specifications). The switch includes numerous security features, including protection against the most common types of attacks.
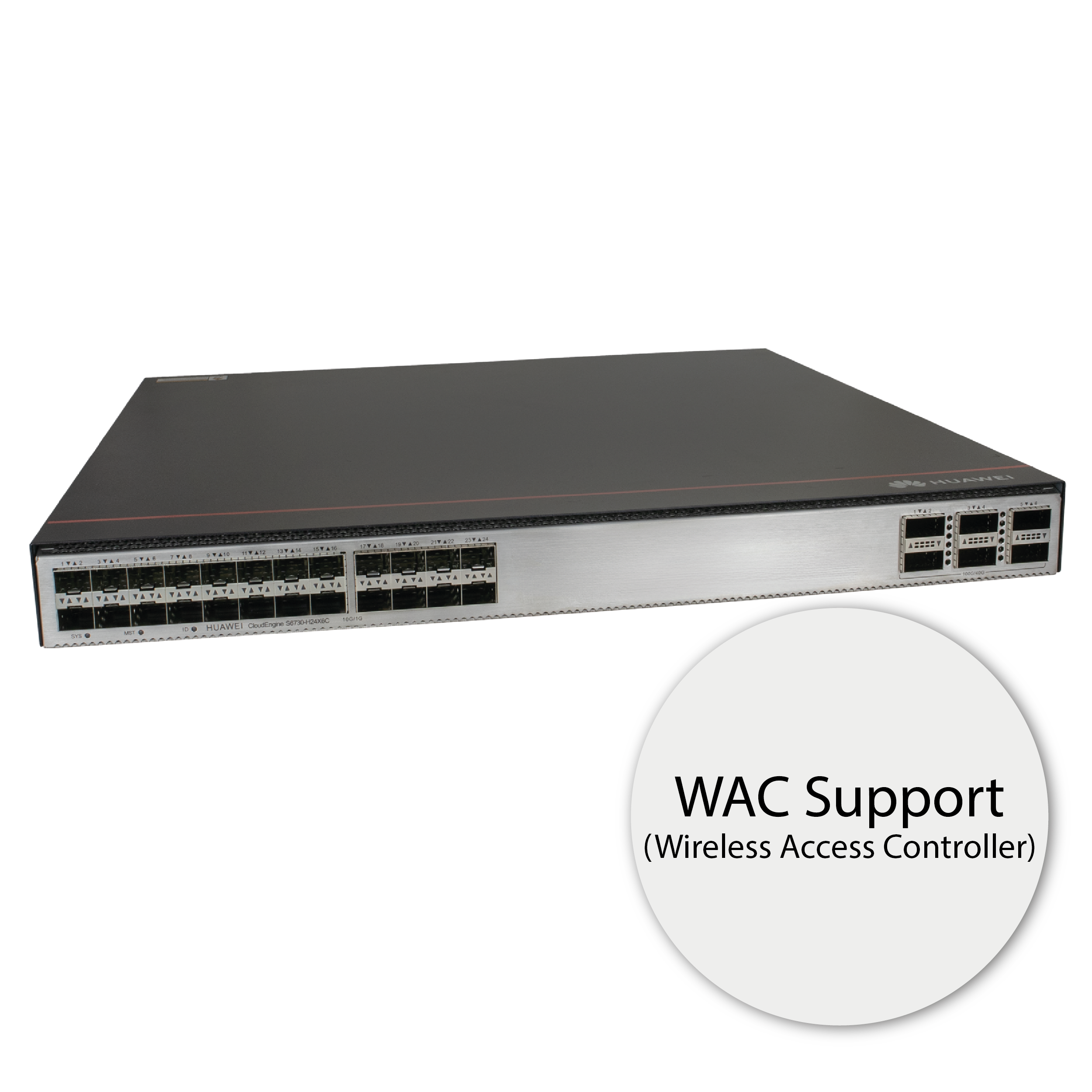
WAC Support
The S6730-H can operate as a WAC (Wireless Access Controller) – a controller for access points. It allows for the management of up to 1000 APs and also supports SVF as a parent switch. SVF (Super Virtual Fabric) technology enables the virtualization of a physical network, where a network composed of core/aggregation switches, access switches, and access points can be virtualized into a single “super switch,” significantly simplifying network management. In large-scale networks, advanced QoS support is also a major advantage – including support for sophisticated control algorithms and queuing mechanisms – ensuring high network performance quality.
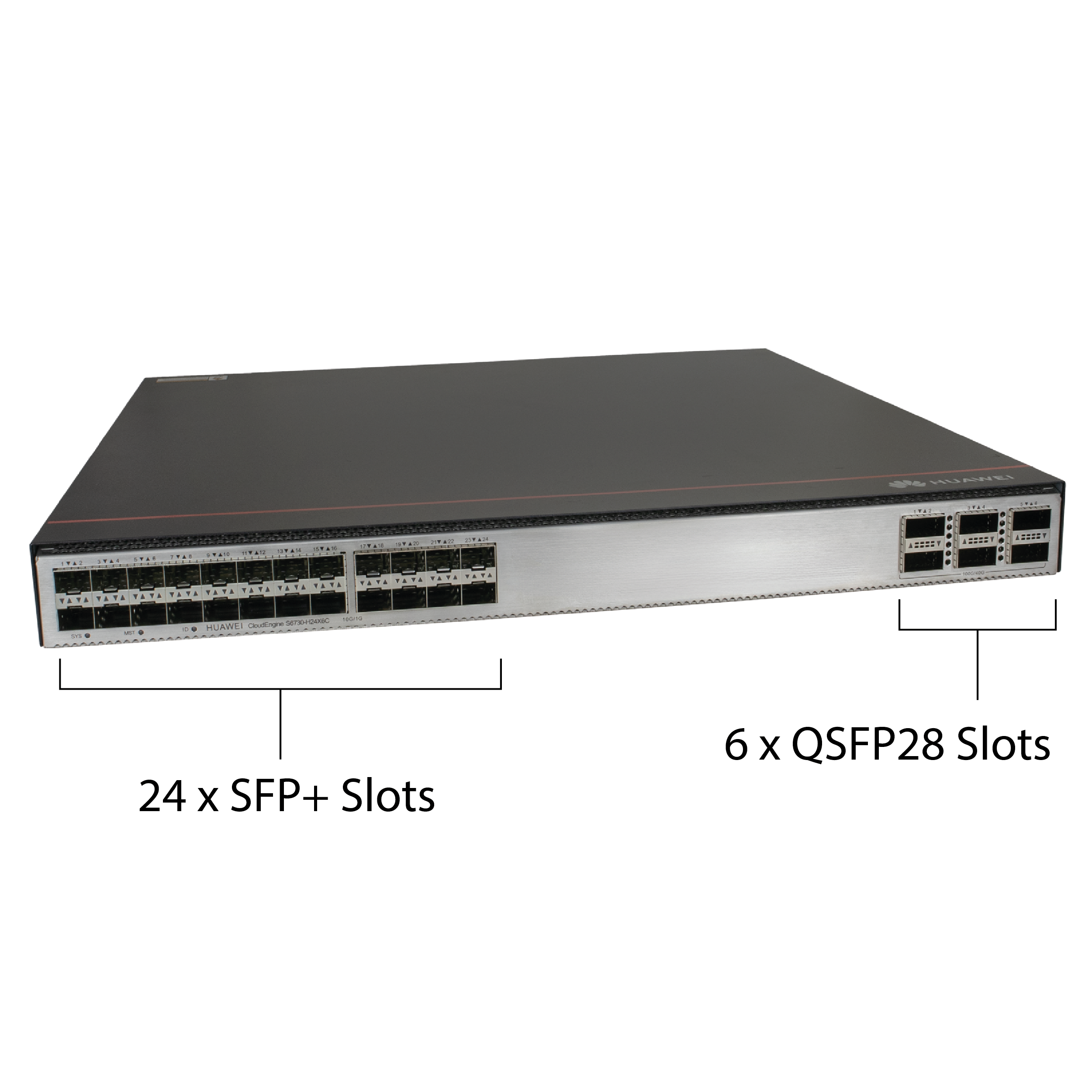


24 sloty SFP+, 6 slotów 24 SFP+ Slots, 6 QSFP28 Slots
The switch features 24 SFP+ slots with a throughput of 10 Gbps and 6 QSFP28 slots with a throughput of 100 Gbps. The total switching capacity reaches an impressive 1.68 Tbps. The device can handle extremely high traffic while maintaining smooth network performance. The S6730-H24 is an excellent solution for environments where the core network infrastructure is built around 10 Gbps bandwidth.
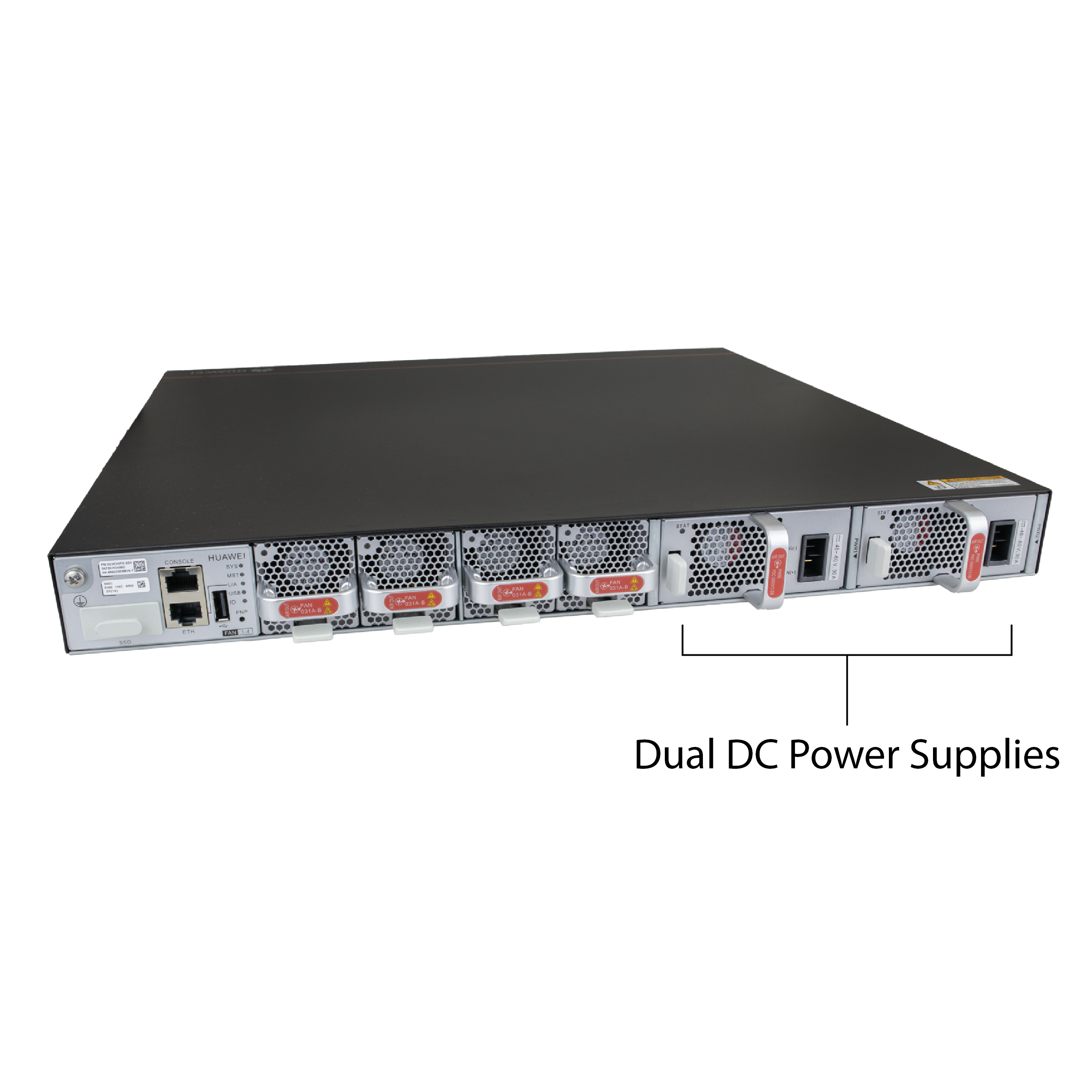
Dual DC Power Supplies
The package includes two PDC1000S12 power supply modules, designed for redundant operation (1+1 power backup). In the event of a failure of one power supply, the other takes over seamlessly. The input voltage range is -48 ~ --60 V DC. The switch’s maximum power consumption under full load is 254 W, while typical power consumption at 30% load is 149 W.
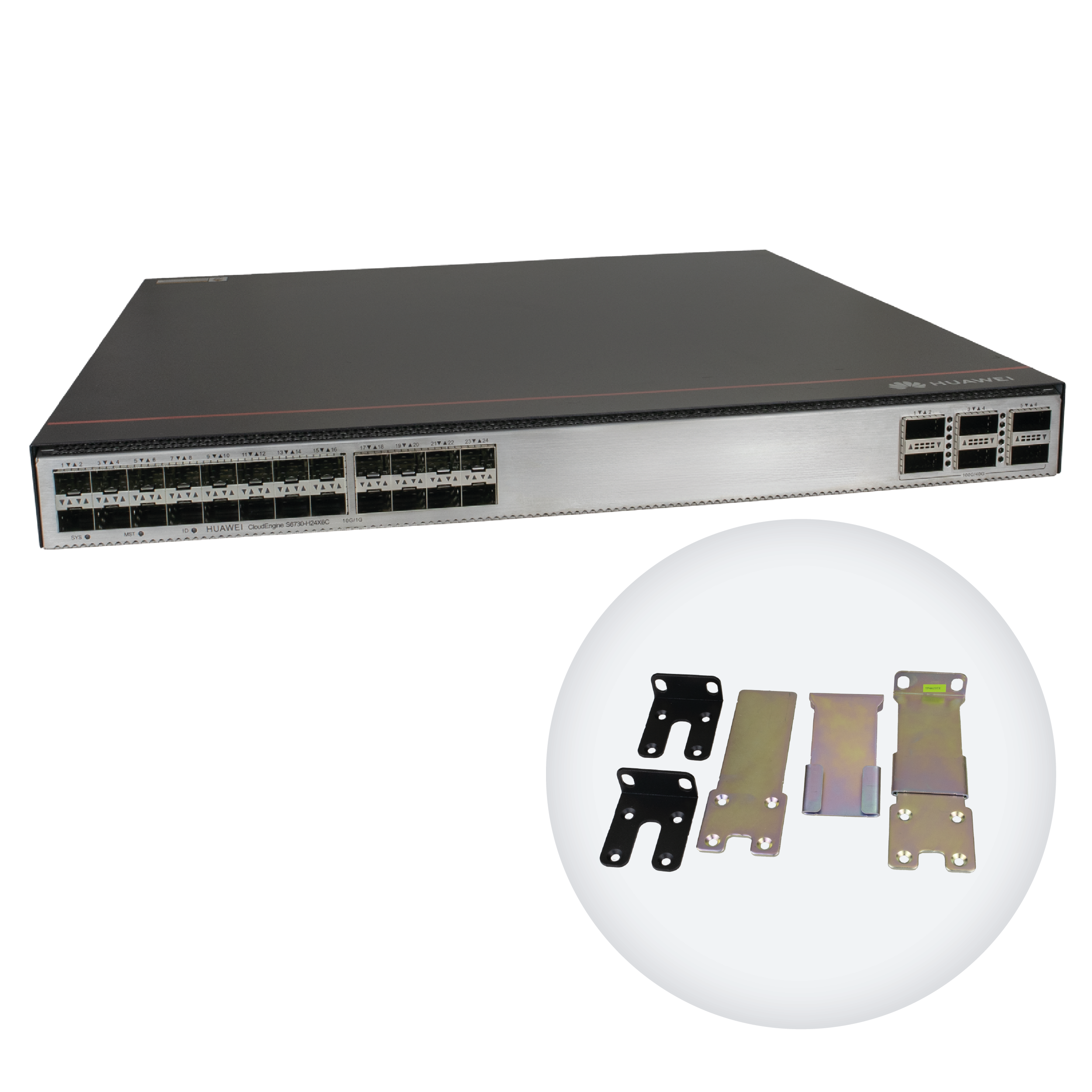


Active cooling, 19" rack enclosure
The switch enclosure is designed for mounting in a 19" rack cabinet, with a height of 1U. The package includes appropriate mounting accessories. The device features 4 fan modules that provide active cooling during operation. Each module can be quickly replaced without the need to disassemble the entire enclosure. The installed fans support front-to-back airflow, drawing air in from the port side and exhausting it out the back of the switch.
Application
Due to its advanced management capabilities and high throughput, the offered product is suitable for a wide range of network environments. One of its primary uses is in internet service provider networks, especially in MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) setups. The device also performs well as an aggregation switch in campus networks, where it can additionally serve as an access point controller. Another application is its use as an access switch in various types of data centers. Regardless of the specific use case, the S6730-H is a device that will be appreciated by many administrators and users.
Specifications
| Huawei S6730-H24X6C | |
| Fixed ports |
24 x 10 Gig SFP+ 6 x 40/100 Gig QSFP28 |
| License |
100 Gb/s N1 Basic Software |
| Dimensions (H x W x D) | 43.6 mm x 442.0 mm x 420.0 mm (1.72 in. x 17.4 in. x 16.5 in.) |
| Chassis height(U) | 1U |
| Voltage |
Rated voltage range: -48 V DC to -60 V DC Maximum voltage range: -38.4 V DC to -72 V DC |
| Maximum input current | 1000 W, 30 A |
| Typical power consumption (30% of traffic load, tested according to ATIS standard) | 149 W |
| Maximum power consumption (100% throughput, full speed of fans) | 254 W |
| Operating temperature | -5°C to +45°C (23°F to 113°F) at an altitude of 0-1800 m (0-5906 ft.) |
| Storage temperature | -40°C to +70°C (-40°F to +158°F) |
| Noise (sound pressure at normal temperature) | < 65 dB(A) |
| Power supply surge protection | ±2 kV in differential mode, ±4 kV in common mode |
| Power supply type | 2x 1000 W DC Power Module |
| Relative humidity | 5% to 95%, noncondensing |
| Fans | 4, Fan modules are pluggable |
| Heat dissipation | Heat dissipation with fan, intelligent fan speed adjustment |
| Service Features | |
|---|---|
| MAC |
Up to 384K MAC address entries IEEE 802.1d standards compliance MAC address learning and aging Static, dynamic, and blackhole MAC address entries Packet filtering based on source MAC addresses |
| VLAN |
4K VLANs Guest VLANs and voice VLANs GVRP MUX VLAN VLAN assignment based on MAC addresses, protocols, IP subnets, policies, and ports VLAN mapping |
| ARP |
Static ARP Dynamic ARP |
| IP routing |
Static routes, RIP v1/2, RIPng, OSPF, OSPFv3, IS-IS, IS-ISv6, BGP, BGP4+, ECMP, routing policy Up to 256K FIBv4 entries Up to 80K FIBv6 entries |
| Interoperability | VLAN-Based Spanning Tree (VBST), working with PVST, PVST+, and RPVST |
| Wireless service |
AP access control, AP domain management, and AP configuration template management Radio management, unified static configuration, and dynamic centralized management WLAN basic services, QoS, security, and user management |
| Ethernet loop protection |
RRPP ring topology and RRPP multi-instance Smart Link tree topology and Smart Link multi-instance, providing millisecond-level protection switchover SEP ERPS (G.8032) BFD for OSPF, BFD for IS-IS, BFD for VRRP, and BFD for PIM STP (IEEE 802.1d), RSTP (IEEE 802.1w), and MSTP (IEEE 802.1s) BPDU protection, root protection, and loop protection |
| MPLS |
MPLS L3VPN MPLS L2VPN (VPWS/VPLS) MPLS-TE MPLS QoS |
| IPv6 features |
Neighbor Discover (ND) PMTU IPv6 Ping, IPv6 Tracert, IPv6 Telnet ACLs based on source IPv6 addresses, destination IPv6 addresses, Layer 4 ports, or protocol types Multicast Listener Discovery snooping (MLDv1/v2) IPv6 addresses configured for sub-interfaces, VRRP6, DHCPv6, and L3VPN |
| Multicast |
IGMP v1/v2/v3 snooping and IGMP fast leave Multicast forwarding in a VLAN and multicast replication between VLANs Multicast load balancing among member ports of a trunk Controllable multicast Port-based multicast traffic statistics IGMP v1/v2/v3, PIM-SM, PIM-DM, and PIM-SSM MSDP Multicast VPN |
| QoS / ACL |
Rate limiting in the inbound and outbound directions of a port Packet redirection Port-based traffic policing and two-rate three-color CAR Eight queues on each port DRR, SP, and DRR+SP queue scheduling algorithms WRED Re-marking of the 802.1p and DSCP fields of packets Packet filtering at Layer 2 to Layer 4, filtering out invalid frames based on the source MAC address, destination MAC address, source IP address, destination IP address, TCP/UDP source/destination port number, protocol type, and VLAN ID Queue-based rate limiting and shaping on ports |
| Security |
Hierarchical user management and password protection DoS attack defense, ARP attack defense, and ICMP attack defense Port isolation, port security, and sticky MAC MAC Forced Forwarding (MFF) Blackhole MAC address entries Limit on the number of learned MAC addresses IEEE 802.1X authentication and limit on the number of users on a port AAA authentication, RADIUS authentication, and HWTACACS authentication NAC SSH V2.0 HTTPS CPU protection Blacklist and whitelist Attack source tracing and punishment for IPv6 packets such as ND, DHCPv6, and MLD packets IPSec for management packet encryption ECA Deception |
| Reliability |
LACP E-Trunk Ethernet OAM (IEEE 802.3ah and IEEE 802.1ag) ITU-Y.1731 DLDP LLDP BFD for BGP, BFD for IS-IS, BFD for OSPF, BFD for static routes |
| SVF |
Acting as the parent node to vertically virtualize downlink switches and APs as one device for management Two-layer client architecture ASs can be independently configured. Services not supported by templates can be configured on the parent node. Third-party devices allowed between SVF parent and clients |
| IPCA |
Marking service packets to obtain the packet loss ratio and number of lost packets in real time Measurement of the number of lost packets and packet loss ratio on networks and devices |
| Management and maintenance |
Cloud-based management Virtual cable test SNMP v1/v2c/v3 RMON Web-based NMS System logs and alarms of different severities GVRP MUX VLAN IEEE 802.3az Automatic power adjustment on Ethernet interfaces NetStream Telemetry |




 Polski
Polski English
English Italiano
Italiano Español
Español Čeština
Čeština Српски
Српски Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Slovenský
Slovenský




