-
€




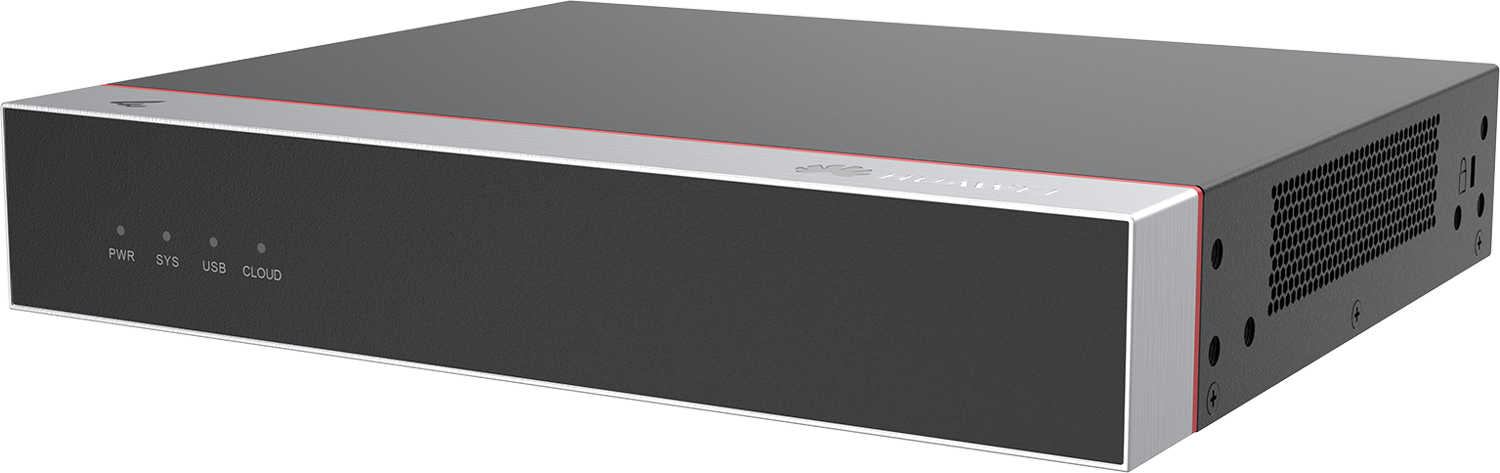
The Huawei AC650-256AP is a device that combines a Wireless Access Controller (WAC) and a switch. It can simultaneously manage up to 256 access points, making it suitable for various types of networks. It is equipped with 10 gigabit Ethernet ports (10/100/1000 Mbps) and 2 SFP+ slots (10 Gbps), capable of handling 10 Gbps traffic, which is crucial for large networks. The AC650-256AP features a built-in AAA/Portal server, providing authentication through a portal or 802.1X. You can configure it in in-path, off-path, bridge, or mesh modes with Layer 2 or Layer 3 connections. It supports backup connections for multiple WACs - 1+1 HSB and N+1 backup. The system provides administrators with rich tools for error detection and diagnostics, greatly facilitating and speeding up centralized network management, such as through quick configuration of connected access points.
Controller for 256 access points
The device is designed to operate as a controller in Huawei wireless systems and can handle up to 256 access points. It supports load balancing using smart roaming, the DFA algorithm for automatic detection of overlapping channels, as well as EDCA and airtime scheduling.
The controller features a built-in portal/AAA server, providing user authentication based on a portal or 802.1X. Authentication covers both wired and wireless users.
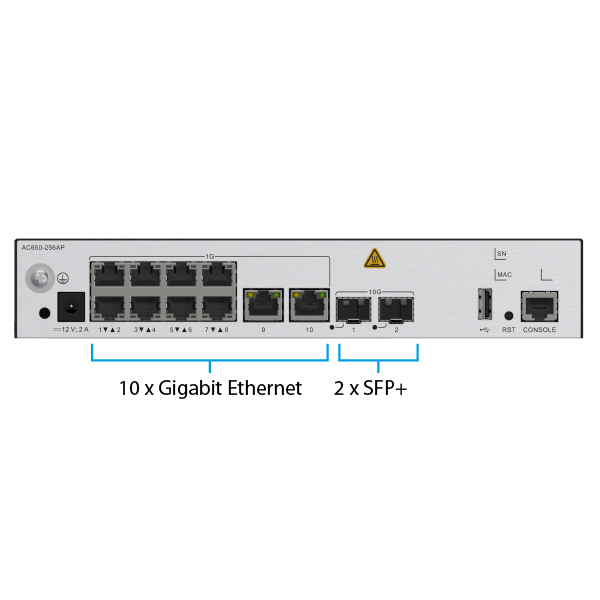

High performance, 2 SFP+ slots, 10 gigabit Ethernet ports
The AC650-256AP is equipped with 2 SFP+ slots with a throughput of 10 Gbps each, along with 10 gigabit Ethernet ports (10/100/1000 Mbps). It has an integrated switch function, which is useful if you are using an in-path configuration.
The device features a high-performance quad-core ARM processor clocked at 1.2 GHz and 2 GB of DDR4 RAM. Depending on the authentication method, it is capable of handling up to 2048 users connected simultaneously.
Advanced monitoring and diagnostics, numerous configuration options
The web interface provides rich capabilities for network monitoring, checking user and access point status, and each radio. In the event of performance degradation, you can quickly identify which segment of the network is malfunctioning. Configuration is simplified with the ability to create profiles and groups of access points. When connecting a new AP, configuration can be copied from another device. With just one click, you can access advanced network diagnostics with suggested solutions for any issues encountered.
The controller can operate in various network modes: in-path, off-path, bridge, or mesh. Access points can be connected at either Layer 2 or Layer 3, depending on the requirements of the location. Additionally, the AC650-256AP supports multiple backup features to ensure operational stability. You can utilize 1+1 HSB and N+1 WAC backup as well as port backups using LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) or MSP (Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol).

Usage
The offered product has been designed for use in large networks where advanced management and convenient monitoring are necessary, allowing for quick configuration and connection of new devices and rapid detection of various errors. External controller deployment also enhances the overall stability of the network; in the case of three devices (controller + router + switch), the workload is evenly distributed among them. Conversely, with a single gateway, there's a risk of it becoming a bottleneck for the entire system.
Specifications
| Huawei AC650-256AP | |
| Performance | |
|---|---|
| Number of managed APs | 256 |
| Number of access users |
2048 (The maximum number of access users varies depending on the authentication mode) |
| Number of MAC address entries | 8192 |
| Forwarding capability | 10 Gb/s |
| Number of VLANs | 4096 |
| Number of routing entries |
IPv4 4096 IPv6: 2048 |
| Number of ARP entries | 4096 |
| Number of multicast forwarding entries | 2048 |
| Number of DHCP IP address pools | 64 IP address pools, each of which contains a maximum of 8192 IP addresses |
| Number of local accounts | 1024 |
| Number of ACLs | 4096 |
| Physical features | |
| Dimensions (H x W x D) | 43.6 mm x 210 mm x 250 mm |
| Interface type | 2 x 10GE optical ports +10 x GE electrical ports 1 x Console (RJ45), 1 x USB |
| Maximum power consumption | 21 W |
| Weight | 1,47 kg |
| Operating temperature and altitude | -60 m to +1800 m: 0°C to 45°C 1800 m to 5000 m: Temperature decreases by 1°C every time the altitude increases 220 m. |
| Relative humidity | 5% RH to 95% RH, noncondensing |
| Power modules | AC/DC adapter |
| Switching and forwarding features | |
| Ethernet features |
Ethernet Operating modes of full duplex, half duplex, and auto-negotiation
VLAN Access modes of access, trunk, and hybrid
MAC Automatic learning and aging of MAC addresses
ARP Static and dynamic ARP entries
LLDP |
| Ethernet loop protection |
MSTP STP |
| IPv4 forwarding |
IPv4 ARP and RARP
Unicast routing Static route
Multicast routing IGMPv1, IGMPv2, and IGMPv3 |
| IPv6 forwarding |
IPv6 ND protocol
Unicast routing Static route
Multicast routing MLD MLD snooping |
| Device reliability | BFD |
| Layer 2 multicast | IGMP snooping Prompt leave Multicast traffic control Inter-VLAN multicast replication |
| Ethernet OAM | Neighbor discovery Link monitoring Fault notification Remote loopback |
| QoS |
Traffic classification Traffic classification based on the combination of the L2 protocol header,
Action Access control after traffic classification
Queue scheduling PQ DRR PQ+DRR WRR PQ+WRR
Congestion avoidance SRED WRED
Application control Smart Application Control (SAC) |
| Configuration and maintenance |
Terminal service Configurations using command lines
File system File systems
Debugging and maintenance Unified management of logs, alarms, and debugging information
Version upgrade Device software loading and online software loading |
| Network management | Different user levels for commands, preventing unauthorized users from accessing device SSHv2.0 RADIUS and HWTACACS authentication for login users ACL filtering DHCP packet filtering (with the Option 82 field) Local attack defense function that can protect the CPU and ensure that the CPU can process services Defense against control packet attacks Defenses against attacks such as source address spoofing, Land, SYN flood (TCP SYN), Smurf, ping flood (ICMP echo), Teardrop, broadcast flood, and Ping of Death attacks IPsec URL filtering Antivirus Intrusion prevention ICMP-based ping and traceroute SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3 Standard MIB RMON NetStream |
| Wireless networking | |
| Networking between APs and WACs | APs and WACs can be connected through a Layer 2 or Layer 3 network. APs can be directly connected to a WAC. APs are deployed on a private network, while WACs are deployed on the public network to implement NAT traversal. WACs can be used for Layer 2 bridge forwarding or Layer 3 routing. WAN authentication escape is supported between APs and WACs. In local forwarding mode, this feature retains the online state of existing STAs and allows access of new STAs when APs are disconnected from WACs, ensuring service continuity. |
| Forwarding mode | Direct forwarding (distributed forwarding or local forwarding) Tunnel forwarding (centralized forwarding) Centralized authentication and distributed forwarding In direct forwarding mode, user authentication packets support tunnel forwarding. Soft GRE forwarding Tunnel forwarding + EoGRE tunnel |
| Wireless networking mode | WDS bridging: Point-to-point (P2P) wireless bridging Point-to-multipoint (P2MP) wireless bridging Automatic topology detection and loop prevention (STP) Wireless mesh network: Access authentication for mesh devices Mesh routing algorithm Zero-configuration provisioning (ZTP) Mesh network with multiple MPPs Vehicle-ground fast link handover Mesh client mode |
| WAC discovery | An AP can obtain the WAC's IP address in any of the following ways: Static configuration DHCP DNS The WAC uses DHCP or DHCPv6 to allocate IP addresses to APs. DHCP or DHCPv6 relay is supported. On a Layer 2 network, APs can discover a WAC by sending broadcast CAPWAP packets. |
| CAPWAP tunnel | Centralized CAPWAP CAPWAP control tunnel and (optional) data tunnel CAPWAP tunnel forwarding and direct forwarding in an extended service set (ESS) Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) encryption, which is enabled by default for the CAPWAP control tunnel Heartbeat detection and tunnel reconnection |
| Active and standby WACs | Enables and disables the switchback function. Supports load balancing. Supports 1+1 HSB. Supports N+1 backup. Supports wireless configuration synchronization between WACs. Supports license sharing between WACs |
| AP management | |
| AP access control | Displays MAC addresses or SNs of APs in the whitelist. Adds a single AP or multiple APs (by specifying a range of MAC addresses or SNs) to the whitelist. Automatically discovers and manually confirms APs. Automatically discovers APs without manually confirming them. |
| AP region management | Supports three AP region deployment modes:
|
| AP profile management | Specifies the default AP profile that is applied to automatically discovered APs |
| AP type management | Manages AP attributes including the number of interfaces, AP types, number of radios, radio types, maximum number of virtual access points (VAPs), maximum number of associated users, and radio gain (for some APs deployed indoors). Provides built-in default AP types. |
| Network topology management | Supports LLDP topology detection. |
| AP working mode management | Supports AP working mode switchover. The AP working mode can be switched to the Fat or cloud mode on the WAC |
| Radio management | |
| Radio profile management | Supports the following parameter settings in a radio profile:
Supports MU-MIMO. |
| Unified static configuration of parameters | Configures radio parameters such as the channel and power of each radio on the WAC and delivers the configurations to APs. |
| Dynamic management | APs can automatically select working channels and power when they go online. In an AP region, APs automatically adjust working channels and power in the event of signal interference:
compensate for the coverage hole. Automatic selection and calibration of radio parameters in AP regions are supported. |
| Enhanced service capabilities | Band steering: enables terminals to preferentially access the 5 GHz frequency band, achieving load balancing between the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands. Smart roaming: enables sticky terminals to roam to APs with better signals.
|
| WLAN service management | |
| ESS management | Allows you to enable SSID broadcast, set the maximum number of access users, and set the association aging time in an ESS. Isolates APs at Layer 2 in an ESS. Maps an ESS to a service VLAN. Associates an ESS with a security profile or a QoS profile. Enables IGMP for APs in an ESS. Supports Chinese SSIDs. |
| VAP-based service management |
Adds multiple VAPs at a time by binding radios to ESSs. Displays information about a single VAP, VAPs with a specified ESS, or all VAPs. Supports configuration of offline APs. Creates VAPs according to batch delivered service provisioning rules in automatic AP discovery mode |
| Automatic service provisioning management | Supports service provisioning rules configured for a specified radio of a specified AP type. Adds automatically discovered APs to the default AP region. The default AP region can be preconfigured. Applies a service provisioning rule to a region to enable APs in the region to go online. |
| Multicast service management |
IGMP snooping IGMP proxy |
| Load balancing | Performs load balancing among radios in a load balancing group. Supports two load balancing modes:
|
| BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) | Identifies device types according to the OUI in the MAC address. Identifies device types according to the user agent (UA) field in an HTTP packet. Identifies device types according to DHCP Option information. Carries device type information in RADIUS authentication and accounting packets. |
| Location services | Locates AeroScout and Ekahau tags. Locates Wi-Fi terminals. Locates Bluetooth terminals. Locates Bluetooth tags. |
| Spectrum analysis | Identifies the following interference sources: Bluetooth, microwave ovens, cordless phones, ZigBee, game controller, 2.4 GHz/5 GHz wireless audio and video devices, and baby monitors. Works with the eSight to display spectrums of interference sources. |
| Hotspot 2.0 | Supports a Hotspot2.0 network. |
| Internet of Things (IoT) | Supports IoT cards on the AP to converge the WLAN and IoT |
| Navi WAC | Supports remote STA access on the Navi WAC. |
| Centralized license control |
Supports a license server as the centralized AP license control point. Allows a license server to manage license clients. Supports license synchronization between a license server and clients |
| WLAN user management | |
| Address allocation of wireless users | Functions as a DHCP server to assign IP addresses to wireless users. |
| WLAN user management | Supports user blacklist and whitelist. Controls the number of access users:
|
| WLAN user roaming | Supports intra-AC Layer 2 roaming. Supports inter-VLAN Layer 3 roaming on a WAC. Supports roaming between WACs. Supports fast key negotiation in 802.1X authentication. Authenticates users who request to reassociate with the WAC and rejects the requests of unauthorized users. Delays clearing user information after a user goes offline so that the user can rapidly go online again. |
| User group management | Supports ACLs. Supports user isolation:
|
| WLAN security | |
| WLAN security profile management | Manages authentication and encryption modes using WLAN security profiles. Binds security profiles to ESS profiles. |
| Authentication modes | Open system authentication with no encryption WEP authentication/encryption WPA/WPA2 authentication and encryption:
WAPI authentication and encryption:
Portal authentication:
|
| Combined authentication | Combined MAC authentication: PSK+MAC authentication MAC+Portal authentication: MAC address-prioritized Portal authentication |
| AAA | Local authentication/local accounts (MAC addresses and accounts) RADIUS authentication Multiple authentication servers:
|
| Security isolation | Port-based isolation User group-based isolation |
| WIDS | Rogue device scan, identification, defense, and containment, which includes dynamic blacklist configuration and detection of rogue APs, STAs, and network attacks. |
| Authority control | ACL limit based on the following:
|
| Other security features | SSID hiding IP source guard: Configures IP and MAC binding entries statically. Generates IP and MAC binding entries dynamically. |
| WLAN QoS | |
| WMM profile management | Enables or disables Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM). Allows a WMM profile to be applied to radios of multiple APs. |
| Traffic profile management |
Manages traffic from APs and maps packet priorities according to traffic profiles. Applies a QoS policy to each ESS by binding a traffic profile to each ESS. |
| AC traffic control | Manages QoS profiles. Uses ACLs to perform traffic classification. Limits incoming and outgoing traffic rates for each user based on inbound and outbound CAR parameters. Limits the traffic rate based on ESSs or VAPs. |
| AP traffic control | Controls traffic of multiple users and allows users to share bandwidth. Limits the rate of a specified VAP. |
| Packet priority configuration |
Sets the QoS priority (IP precedence or DSCP priority) for CAPWAP control channels. Sets the QoS priority for CAPWAP data channels:
|
| Airtime fair scheduling | Allocates equal time to users for occupying the channel, which improves users' Internet access experience. |




 Polski
Polski English
English Italiano
Italiano Español
Español Čeština
Čeština Српски
Српски Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Slovenský
Slovenský




