-
zł


Huawei S6750-H48Y8C is an enterprise-class switch from the CloudEngine family. It features 48 SFP28 (25 Gbps) slots and 8 QSFP28 (100 Gbps) slots, offering top-tier management capabilities in its generation. It is designed to operate as a core or aggregation switch and differs from the S6730 series switches by supporting segment routing — SRv6 BE and BGP EVPN — as well as MACsec implementation. In addition, it supports all the features of the S6730, such as BGP and BGP4+, MPLS, and includes advanced security mechanisms. It can also function as a WAC — Wireless Access Controller — and act as a controller for access points, helping to reduce the number of devices used in the network. The device is designed for use in ISP environments, as an aggregation switch in large campus networks, or as a core switch in small and medium-sized campus networks. Thanks to its rich management features and high throughput, the S6750-H48Y8C can also be successfully deployed in other scenarios and locations.
The device features a chassis designed for mounting in a 19" rack, and the necessary mounting accessories are included in the package. It uses active cooling with five fan modules and a front-to-back airflow system — air is drawn in from the port side and expelled at the rear. The package includes one PAC1K2S12 power module and one PDC1K2S12 module. These modules can operate redundantly, with the second module taking over in case of a failure of the first. The input voltage range for the PAC1K2S12 is 100 - 240 V AC, while for the PDC1K2S12, it is -48 ~ -60 V DC. The maximum power consumption of the switch is 200 W, and the typical power consumption at 30% load is 165 W.

CloudEngine S6750-H Series
The offered product is a switch from the CloudEngine S6750-H series. It provides the same features as the S6730 series, supporting routing including BGP and BGP4+, allowing real-time network quality monitoring and error detection. It utilizes IFIT (In-situ Flow Information Telemetry) — a technology that uses special packets to measure the actual performance of IP networks, including packet loss and latency. There are three available IFIT modes: application-level, tunnel-level, and native-IP, each responsible for measuring different network layers. The switch supports VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol), enabling the implementation of backup uplink connections. The S6750-H can be connected to multiple other switches through multiple links. It also supports more advanced features than the S6730-H, including segment routing (SRv6 BE, BGP EVPN) and MACsec.
The device supports iStack — intelligent stacking, allowing several switches to be combined into a single unit (from a management perspective). You can access the management panel via the cloud or through one of many other available methods (see the specification for a full list). The switch also includes numerous security features, including protection against the most common types of attacks.WAC Support
The S6750-H can operate as a WAC (Wireless Access Controller), enabling management of up to 1,000 access points. It supports encrypted CAPWAP tunnels and many other useful features, which are listed in the specifications. In large networks, an important advantage is its advanced QoS support, with traffic classification based on L2 headers, L3 protocols, L4 protocols, and 802.1p priority.

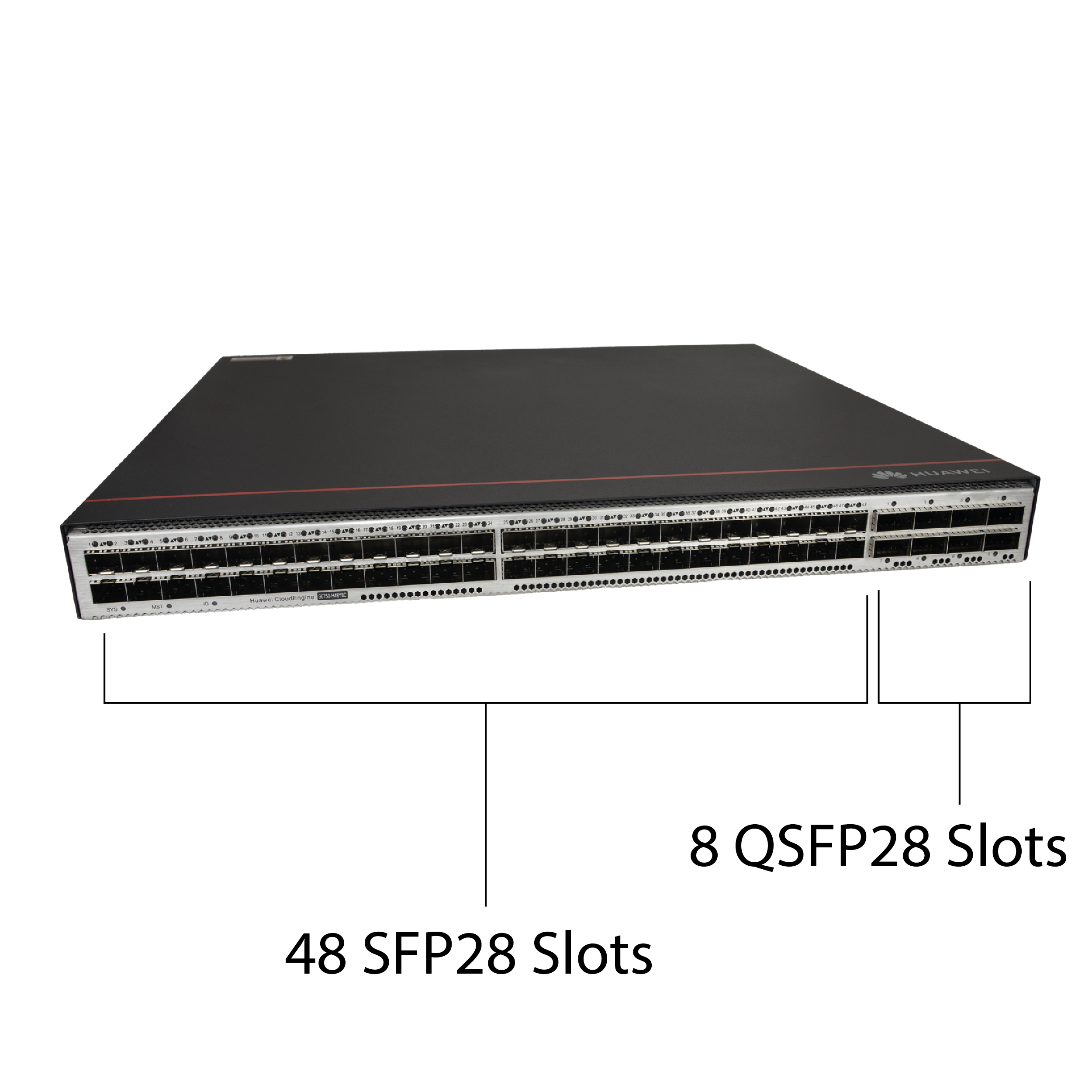
48 SFP28 Slots, 8 QSFP28 Slots
The switch features 48 SFP28 slots with a maximum throughput of 25 Gbps and 8 QSFP28 slots with 100 Gbps throughput. The SFP28 slots also support 1G and 10G modes, while the QSFP28 slots additionally support 40G mode. The total switching capacity reaches up to 4 Tbps, and the overall system performance is 8 Tbps. The device can handle extremely high traffic while maintaining smooth operation, making it an excellent choice for large networks where other solutions may fall short. Moreover, it enables you to build a network infrastructure based on 25 Gbps throughput.
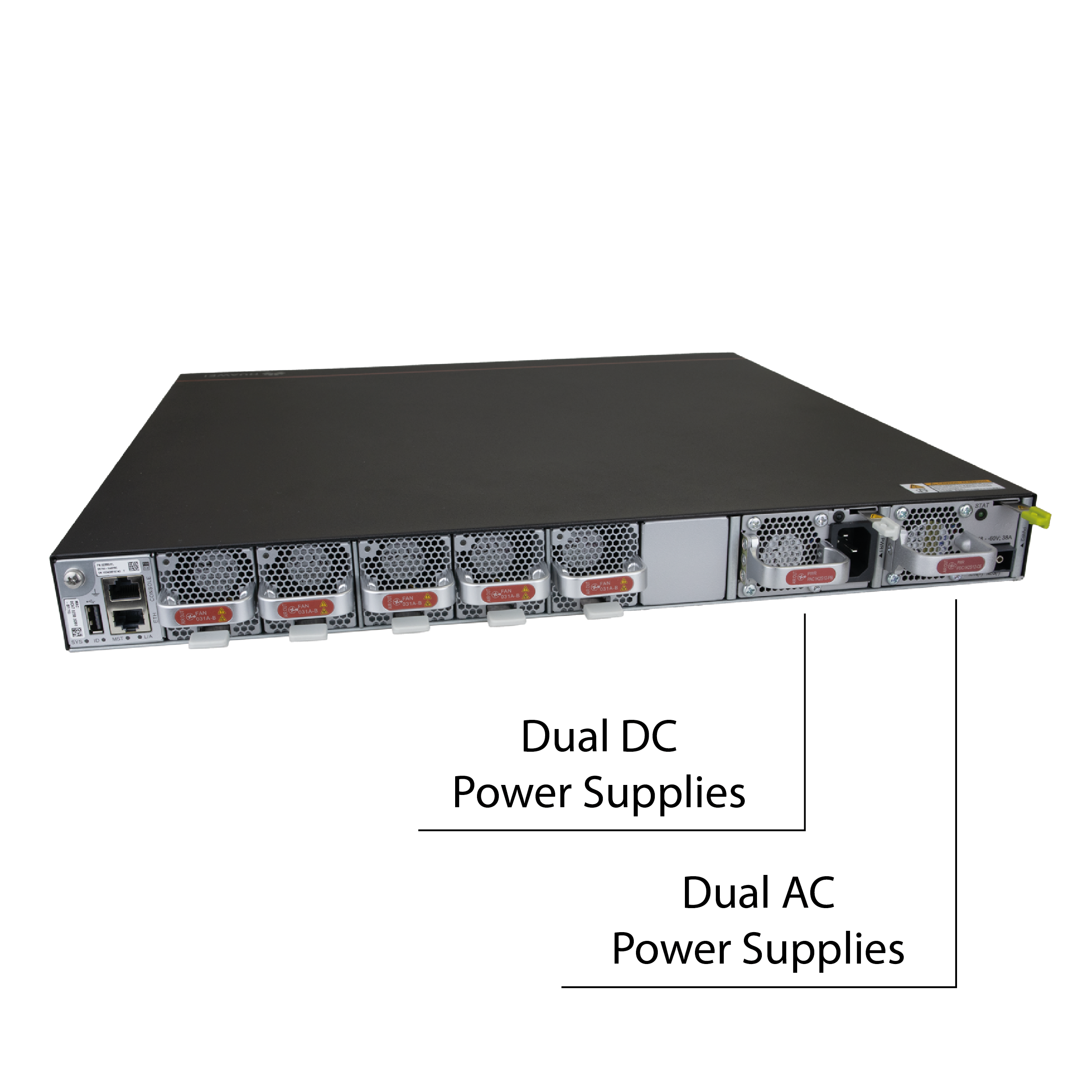
One AC Power Supply, One DC Power Supply
The package includes two power modules: one PAC1K2S12 and one PDC1K2S12, designed for redundant operation (1+1 power backup). In the event of a failure of one power supply, the other takes over. The input voltage range for the PAC1K2S12 is 100 - 240 V AC, while the input voltage range for the PDC1K2S12 is -48 ~ -60 V DC. The maximum power consumption of the switch under full load is 200 W, and the typical power consumption at 30% load is 165 W. Using one DC power supply is ideal for locations where a backup power supply or a telecommunications power station is available in the rack.

Active Cooling, 19" Rack-Mountable Chassis
The switch's chassis is designed for installation in a 19" rack and has a height of 1U. The package includes appropriate mounting accessories. The device is equipped with five hot-swappable fan modules that provide active cooling during operation. Each module can be quickly replaced without powering down the device or disassembling the chassis. The fans support front-to-back airflow — air is drawn in from the port side and expelled at the rear of the switch.
Application
The switch supports advanced management, offering very high throughput and performance, making it ideal for demanding applications and large networks. It can be successfully used in Internet Service Provider networks, particularly in MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) environments. The device can be used as an aggregation switch in large campus networks or as a core switch in small and medium-sized campus networks. The applications of the S6750-H extend far beyond what the manufacturer initially envisioned. Due to its high throughput, the switch can be effectively deployed in many other networks, meeting the needs of numerous administrators and users.
Specifications
| Huawei S6750-H48Y8C | |
| Hardware | |
|---|---|
| Chassis dimensions (H x W x D, mm) | 43.6 mm x 442.0 mm x 420.0 mm (1.72 in. x 17.4 in. x 16.54 in.) |
| Chassis height | 1U |
| Chassis weight (full configuration weight, including weight of packaging materials) | 11.23 kg |
| Fixed ports |
48x SFP28 slot (1 / 10 / 25 Gb/s) 8x QSFP28 slot (40 / 100 Gb/s) |
| Management port |
ETH management port Console port (RJ45) USB port |
| CPU |
Frequency: 1,4 GHz Cores: 4 |
| Memory |
Memory (RAM): 8 GB Flash: 4 GB |
| Power supply type |
1x 1200 W AC 1x 1200 W DC |
| Rated voltage range |
AC: 100 V AC to 240 V AC; 50/60 Hz HVDC: 240 V DC DC: –48 V DC to –60 V DC |
| Maximum voltage range |
AC: 90 V AC to 290 V AC; 45–65 Hz HVDC: 190 V DC to 290 V DC DC: -38.4 V DC to -72 V DC |
| Maximum input current |
AC: 100 V - 130 V AC: 10 A 200 V - 240 V AC: 8 A HVDC: 240 V DC: 8 A DC: 38 A |
| Typical power consumption (30% of traffic load, tested according to ATIS standard) | 166 W |
| Maximum power consumption (100% throughput, full speed of fans) | 200 W |
| Heat dissipation mode | Air cooling for heat dissipation, intelligent fan speed adjustment |
| Number of fan modules | 5 |
| Airflow | Air intake from front, air exhaustion from rear (front-to-rear) |
| Long-term operating temperature | 0-1800 m: -5°C to 45°C 1800-5000 m: The operating temperature decreases 1°C for every 220 m increase in altitude. |
| Storage temperature | -40°C ~ 70°C |
| Relative humidity | 5% to 95%, noncondensing |
| Operating altitude | 0 - 5000 m |
| Noise under normal temperature (sound power) | 58.4 dB(A) |
| Noise under high temperature (sound power) | 82.1 dB(A) |
| Noise under normal temperature (sound pressure) | 57.2 dB(A) |
| Surge protection specification (power port) |
AC: ±6 kV in differential mode, ±6 kV in common mode DC: ±2 kV in differential mode, ±4 kV in common mode |
| MTBF (year) | 29.72 |
| MTTR (hour) | 2 |
| Availability | > 0.99999 |
| Service Features | |
| User management |
Unified user management 802.1X authentication MAC authentication Traffic- and duration-based accounting User authorization based on user groups, domains, and time ranges Jumbo frames:9500 bytes |
| MAC |
Automatic MAC address learning and aging 512K MAC entries (MAX) Static, dynamic, and blackhole MAC address entries Source MAC address filtering MAC address learning limiting based on ports and VLANs |
| VLAN |
4K VLANs Access mode, Trunk mode and Hybrid mode Default VLAN QinQ and enhanced selective QinQ VLAN Stacking, VLAN mapping Dynamic VLAN assignment based on MAC addresses |
| ARP | ARP Snooping |
| DHCP |
DHCPv4 Client/Relay/Server, DHCPv4 Snooping DHCPv6 Client/Relay/Server, DHCPv6 Snooping |
| IP routing |
IPv4 dynamic routing protocols such as RIP, OSPF, IS-IS, and BGP IPv6 dynamic routing protocols such as RIPng, OSPFv3, ISISv6, and BGP4+ Routing Policy, Policy-Based Routing VRF |
| Segment Routing |
SRv6 BE (L3 EVPN) BGP EVPN SRv6 configuration through NETCONF |
| Multicast |
IGMPv1/v2/v3 and IGMP v1/v2/v3 Snooping PIM-DM, PIM-SM, PIM-SSM, PIMv6 Fast-leave mechanism Multicast traffic control Multicast querier Multicast protocol packet suppression |
| MPLS |
MPLS-LDP MPLS-L3VPN MPLS Qos |
| QoS |
Traffic classification based on Layer 2 headers, Layer 3 protocols, Layer 4 protocols, and 802.1p priority Actions such as ACL, Committed Access Rate (CAR), re-marking, and scheduling Queuing algorithms, such as PQ, DRR, WDRR, and PQ+DRR, PQ+WDRR Congestion avoidance mechanisms such as WRED and tail drop Traffic shaping Eight queues on each interface Network Slicing |
| Native-IP IFIT |
Marks the real service packets to obtain real-time count of dropped packets and packet loss ratio The statistical period can be modified Two-way frame delay measurement |
| Ethernet loop protection |
STP (IEEE 802.1d), RSTP (IEEE 802.1w), and MSTP (IEEE 802.1s). BPDU protection, root protection, and loop protection G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection Switching (ERPS) Smart Ethernet Protection(SEP) |
| Reliability |
M-LAG(switching time < 2s) Service interface-based stacking Maximum number of stacked devices Stack bandwidth (Bidirectional) Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) and E-Trunk Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) and Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) for VRRP BFD for BGP/IS-IS/OSPF/static routes Eth-OAM 802.1ag(CFM) Smartlink LLDP LBDT Y.1731 |
| System management |
iStack, Maximum number: 9 Console terminal service Telnet/IPv6 Telnet terminal service SSH v1.5 SSH v2.0 SNMP v1/v2c/v3 FTP, TFTP, SFTP BootROM upgrade and remote in-service upgrade Hot patch User operation logs Open Programmability System (OPS) Streaming Telemetry GVRP iPCA, NetStream, NQA, Telemetry 1588v2 |
| Security and management |
NAC Port security RADIUS and HWTACACS authentication for login users MACsec Command line authority control based on user levels, preventing unauthorized users from using command configurations Defense against DoS attacks, Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) SYN Flood attacks, User Datagram Protocol (UDP) Flood attacks, broadcast storms, and heavy traffic attacks IPv6 RA Guard CPU hardware queues to implement hierarchical scheduling and protection for protocol packets on the control plane Remote Network Monitoring (RMON) Secure boot Port mirroring ND snooping |
| Wireless management (integrated WLAN AC): Basic WLAN services |
Hot backup for devices with integrated WLAN AC functionality in cluster mode 2.4G & 5G load balancing 5G-prior access |
| Wireless management (integrated WLAN AC): AP management |
Total number of managed APs: 1K An IPv4 network between an AP and a WLAN AC AP blacklist AP whitelist Sets the AP access control mode AP configuration and management AP LLDP topology awareness
|
| Wireless management (integrated WLAN AC): Wireless user management |
User roaming within a WLAN AC AP-based user location 802.1X authentication MAC address authentication Portal authentication |
| Wireless management (integrated WLAN AC): CAPWAP |
Direct data forwarding on L2/L3 networks Tunnel-based data forwarding on L2/L3 networks CAPWAP tunnel encryption |
| Wireless management (integrated WLAN AC): RF management |
802.11a/b/g/n 802.11ac wave1/wave2 802.11ax Sets RF interference monitoring and avoidance Detects co-channel interference, adjacent interference, and interference from other devices and STAs Automatically selects channels and power when APs go online Dynamic power and channel optimization |
| Wireless management (integrated WLAN AC): WLAN QoS |
Rate limiting of upstream and downstream traffic on the air interface based on the VAP Rate limiting of upstream and downstream traffic on the air interface based on users CAR for WLAN users |




 Polski
Polski English
English Italiano
Italiano Español
Español Čeština
Čeština Српски
Српски Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Slovenský
Slovenský




